Heating, Ventilation, & Air Conditioning (HVAC)
High-Efficiency Systems
Mini Split - Ductless
-
Ductless mini split systems are a great, energy efficient option for heating and cooling your home. Rather than moving conditioned air through ducting systems, ductless mini splits simply circulate air within a room through the unit head (pictured above). The air is heated or cooled (depending on the needs of the space) by using a heat pump. Refrigerant line sets are installed between the unit head and the heat pump unit located on the exterior of the building. If you are looking for a simple, energy efficient way to heat your home that does not require a ducting system, then a mini split is a great option.
One drawback of ductless mini split systems is that they do not introduce fresh air from outside the building or room, which is why it is a good idea to couple these systems with an ERV (see above). Additionally the air filtration system on these units is generally inferior to those found on a typical ducted air conditioning system.
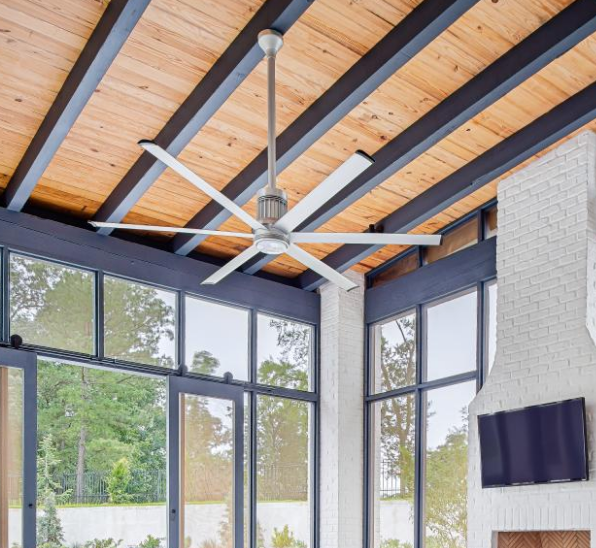
Ceiling Fan
-
Ceiling fans are a great choice for mixing air in large rooms, particularly those with high ceilings. In winter months they help to move hot air that has risen up to the ceiling back down to lower parts of the room. In summer months they help to circulate cool air from the air conditioning system and create a cooling effect through evaporation. If you have high ceilings in your home, a ceiling fan is a energy efficient option for optimizing your heating and cooling systems. One of our favorite brands of high efficiency ceiling fans is Big Ass Fans.
Fans do not themselves introduce warm or cool air into a space, so it’s important to couple them with other heating and cooling systems.
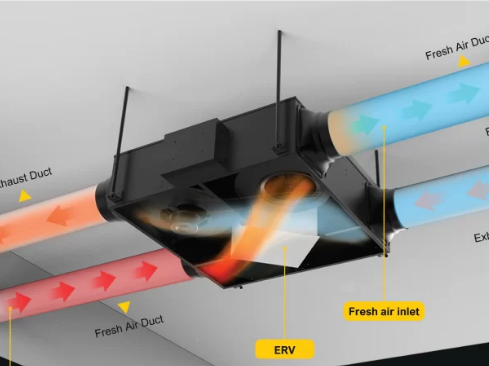
Energy-Recovery Ventilator (ERV)
-
An energy recovery ventilator (ERV) is a type of heat recovery ventilator (HRV), which is a ventilation system that recovers energy by operating between two air sources at different temperatures. It is used to reduce the heating and cooling demands of buildings.
By recovering the residual heat in the exhaust gas, the fresh air introduced into the air conditioning system is preheated (or pre-cooled) before it enters the room, or the air cooler of the air conditioning unit performs heat and moisture treatment. A typical heat recovery system in buildings comprises a core unit, channels for fresh and exhaust air, and blower fans. Building exhaust air is used as either a heat source or heat sink, depending on the climate conditions, time of year, and requirements of the building. Heat recovery systems typically recover about 60–95% of the heat in the exhaust air and have significantly improved the energy efficiency of buildings.
These units are particularly important to use in new construction homes which are often built air-tight to improve energy efficiency. They also couple well with ductless mini split systems.
Wood & Gas Stoves
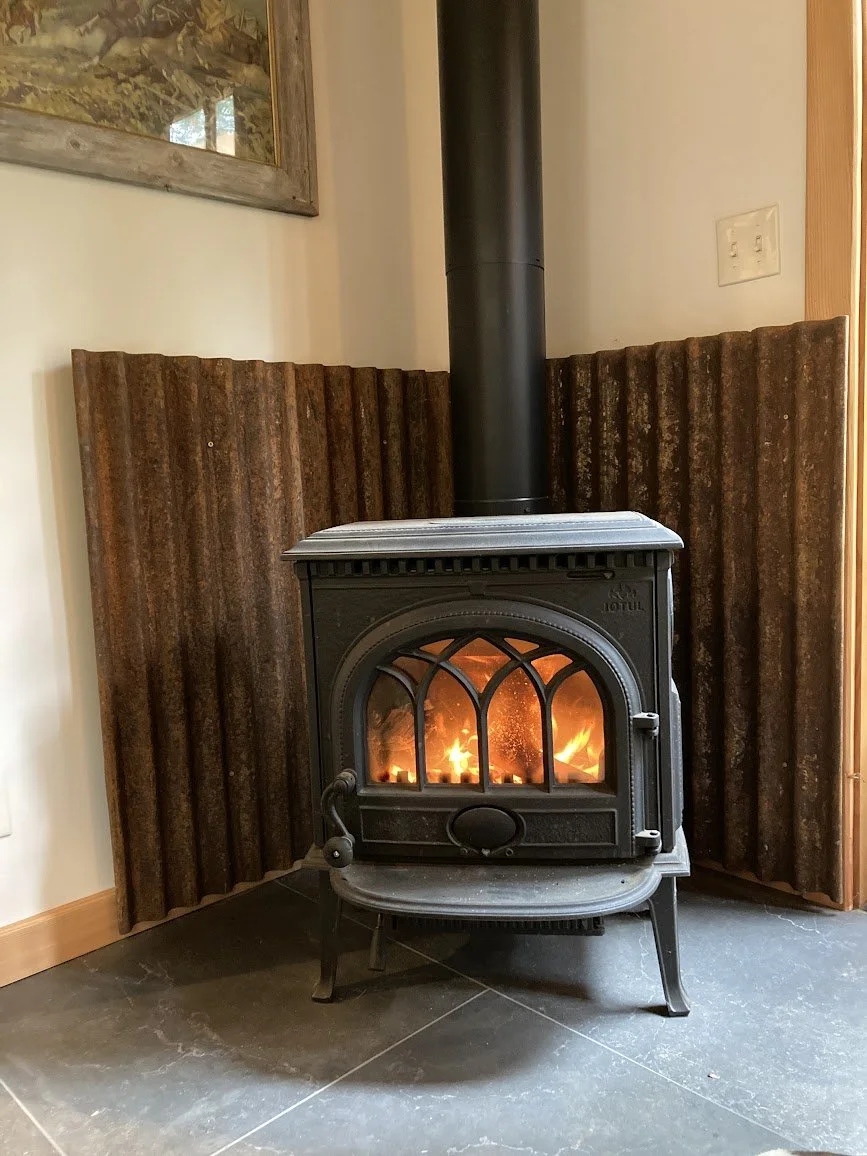
Wood Stove - Free Standing
-
Wood burning stoves are a great option for homes located in forested regions. They come as insert units or free standing (pictured above). Heat from wood burning stoves is particularly dry and can heat a space in a very short amount of time. Wood burning stoves provide a special ambiance that cannot be found in any other heating system. In forested regions, there is typically an abundance of dead wood that needs to be dealt with for wildfire safety, so why not use it to heat your home. Wood burning stoves are also a great alternative heating source incase the power grid goes out.
We recommend coupling these units with and additional heating source, since these units will not maintain a minimum room temperature if no one is home to keep the fire going. We also recommend installing an air-intake on these units as it helps them operate more efficiently.
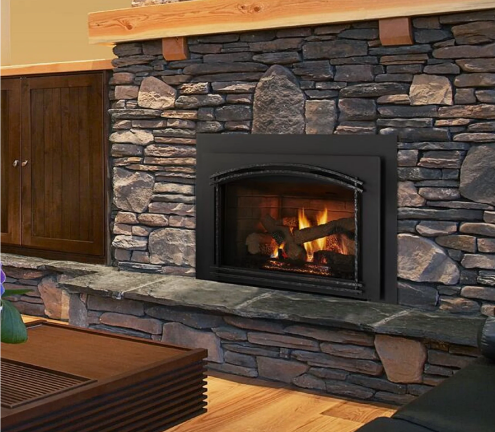
Gas Stove - Insert
-
Gas burning stoves are a great option when you are looking to create the ambiance of a wood burning stove without the hassle of collecting firewood. These units can come free standing or as an insert (pictured above). Though not as dry and hot as the heat from wood burning stoves, gas stoves have the added benefit of being attached to a thermostat and maintaining a minimum room temperature even if no one is home to keep the fire going.
One drawback to these units is that they often require power to operate, which makes them useless during power outages. Additionally, they operate on natural gas or propane which can both be quite expensive and are both fossil fuels that contribute to climate change.